Xenazine
Generic name: tetrabenazine
Drug class: VMAT2 inhibitors
Medically reviewed by A Ras MD.
What is Xenazine?
Xenazine is a medicine that is used to treat the involuntary movements (chorea) of Huntington’s disease. Xenazine does not cure the cause of the involuntary movements, and it does not treat other symptoms of Huntington’s disease, such as problems with thinking or emotions.
It is not known whether Xenazine is safe and effective in children.
Description
XENAZINE (tetrabenazine) is a monoamine depletor for oral administration. The molecular weight of tetrabenazine is 317.43; the pKa is 6.51. Tetrabenazine is a hexahydro-dimethoxy-benzoquinolizine derivative and has the following chemical name: cis rac –1,3,4,6,7,11b-hexahydro-9,10-dimethoxy-3-(2-methylpropyl)-2H-benzo[a]quinolizin-2-one.
The empirical formula C19H27NO3 is represented by the following structural formula:
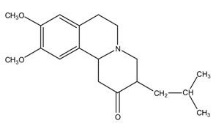
Tetrabenazine is a white to slightly yellow crystalline powder that is sparingly soluble in water and soluble in ethanol.
Each XENAZINE (tetrabenazine) tablet contains either 12.5 or 25 mg of tetrabenazine as the active ingredient.
XENAZINE (tetrabenazine) tablets contain tetrabenazine as the active ingredient and the following inactive ingredients: lactose, magnesium stearate, maize starch, and talc. The 25 mg strength tablet also contains yellow iron oxide as an inactive ingredient.
XENAZINE (tetrabenazine) tablets are supplied as a yellowish-buff, scored tablet containing 25 mg of tetrabenazine or as a white, non-scored tablet containing 12.5 mg of tetrabenazine.
Mechanism of Action
The precise mechanism by which XENAZINE (tetrabenazine) exerts its anti-chorea effects is unknown but is believed to be related to its effect as a reversible depletor of monoamines (such as dopamine, serotonin, norepinephrine, and histamine) from nerve terminals. Tetrabenazine reversibly inhibits the human vesicular monoamine transporter type 2 (VMAT2) (Ki ≈ 100 nM), resulting in decreased uptake of monoamines into synaptic vesicles and depletion of monoamine stores. Human VMAT2 is also inhibited by dihydrotetrabenazine (HTBZ), a mixture of α-HTBZ and β-HTBZ. α- and β-HTBZ, major circulating metabolites in humans, exhibit high in vitro binding affinity to bovine VMAT2. Tetrabenazine exhibits weak in vitro binding affinity at the dopamine D2 receptor (Ki = 2100 nM).
What is the most important information I should know about Xenazine?
- Xenazine can cause serious side effects, including:
- depression
- suicidal thoughts
- suicidal actions
- You should not start taking Xenazine if you are depressed (have untreated depression or depression that is not well controlled by medicine) or have suicidal thoughts.
- Pay close attention to any changes, especially sudden changes, in mood, behaviors, thoughts or feelings. This is especially important when Xenazine is started and when the dose is changed.
Call the doctor right away if you become depressed or have any of the following symptoms, especially if they are new, worse, or worry you:
- feel sad or have crying spells
- lose interest in seeing your friends or doing things you used to enjoy
- sleep a lot more or a lot less than usual
- feel unimportant
- feel guilty
- feel hopeless or helpless
- more irritable, angry or aggressive than usual
- more or less hungry than usual or notice a big change in your body weight
- have trouble paying attention
- feel tired or sleepy all the time
- have thoughts about hurting yourself or ending your life
Who should not take Xenazine?
Do not take Xenazine if you:
- are depressed or have thoughts of suicide. See “What is the most important information I should know about Xenazine?”
- have liver problems.
- are taking a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) medicine. Ask your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure.
- are taking reserpine. Do not take medicines that contain reserpine (such as Serpalan and Renese-R) with Xenazine. If your doctor plans to switch you from taking reserpine to Xenazine, you must wait at least 20 days after your last dose of reserpine before you start taking Xenazine.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking Xenazine?
Tell your doctor about all your medical conditions, including if you:
- have emotional or mental problems (for example, depression, nervousness, anxiety, anger, agitation, psychosis, previous suicidal thoughts or suicide attempts).
- have liver disease.
- have any allergies. See the end of this Medication Guide for a complete list of the ingredients in Xenazine.
- have breast cancer or a history of breast cancer.
- have heart disease that is not stable, have heart failure or recently had a heart attack.
- have an irregular heartbeat (cardiac arrhythmia).
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if Xenazine can harm your unborn baby.
- are breastfeeding. It is not known if Xenazine passes into breast milk.
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take, including prescription medicines and nonprescription medicines, vitamins and herbal products. Using Xenazine with certain other medicines may cause serious side effects. Do not start any new medicines while taking Xenazine without talking to your doctor first.
How should I take Xenazine?
- Xenazine is a tablet that you take by mouth.
- Take Xenazine exactly as prescribed by your doctor.
- You may take Xenazine with or without food.
- Your doctor will increase your dose of Xenazine each week for several weeks, until you and your doctor find the best dose for you.
- If you stop taking Xenazine or miss a dose, your involuntary movements may return or worsen in 12 to 18 hours after the last dose.
- Before starting Xenazine, you should talk to your healthcare provider about what to do if you miss a dose. If you miss a dose and it is time for your next dose, do not double the dose.
- Tell your doctor if you stop taking Xenazine for more than 5 days. Do not take another dose until you talk to your doctor.
- If your doctor thinks you need to take more than 50 mg of Xenazine each day, you will need to have a blood test to see if it is safe for you.
What should I avoid while taking Xenazine?
Sleepiness (sedation) is a common side effect of Xenazine. While taking Xenazine, do not drive a car or operate dangerous machinery until you know how Xenazine affects you. Drinking alcohol and taking other drugs that may also cause sleepiness while you are taking Xenazine may increase any sleepiness caused by Xenazine.
What are the possible side effects of Xenazine?
Xenazine can cause serious side effects, including:
- Depression, suicidal thoughts, or actions. See “What is the most important information I should know about Xenazine?”
- Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS). Call your doctor right away and go to the nearest emergency room if you develop these signs and symptoms that do not have another obvious cause:
- high fever
- stiff muscles
- problems thinking
- very fast or uneven heartbeat
- increased sweating
- Parkinsonism. Symptoms of Parkinsonism include: slight shaking, body stiffness, trouble moving or keeping your balance.
- Restlessness. You may get a condition where you feel a strong urge to move. This is called akathisia.
- Irregular heartbeat. Xenazine increases your chance of having certain changes in the electrical activity in your heart which can be seen on an electrocardiogram (EKG). These changes can lead to a dangerous abnormal heartbeat. Taking Xenazine with certain medicines may increase this chance.
- Dizziness due to blood pressure changes when you change position (orthostatic hypotension). Change positions slowly from lying down to sitting up and from sitting up to standing when taking Xenazine. Tell your doctor right away if you get dizzy or faint while taking Xenazine. Your doctor may need to watch your blood pressure closely.
Common side effects with Xenazine include:
- sleepiness (sedation)
- trouble sleeping
- depression
- tiredness (fatigue)
- anxiety
- restlessness
- agitation
- nausea
Tell your doctor if you have any side effects. Do not stop taking Xenazine without talking to your doctor first.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) at 1-800-FDA-1088.
General information about the safe and effective use of Xenazine
Xenazine contains the active ingredient tetrabenazine. It also contains these inactive ingredients: lactose, maize starch, talc, and magnesium stearate. The 25 mg tablet, which is pale yellow, also contains yellow iron oxide.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use Xenazine for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Xenazine to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. Keep Xenazine out of the reach of children.
This Medication Guide summarizes the most important information about Xenazine. If you would like more information, talk with your doctor. You can ask your doctor or pharmacist for information about Xenazine that is written for healthcare professionals. You can also call Lundbeck’s Xenazine Information Center at 1-888-882-6013 (option 1) or visit www.xenazineusa.com.
What are the ingredients in Xenazine?
Active ingredient: tetrabenazine
Inactive ingredients:
White 12.5mg tablets: unspecified form lactose, magnesium stearate, corn starch, talc
Yellow 25mg tablets: unspecified form lactose, magnesium stearate, corn starch, talc, ferric oxide yellow
Label
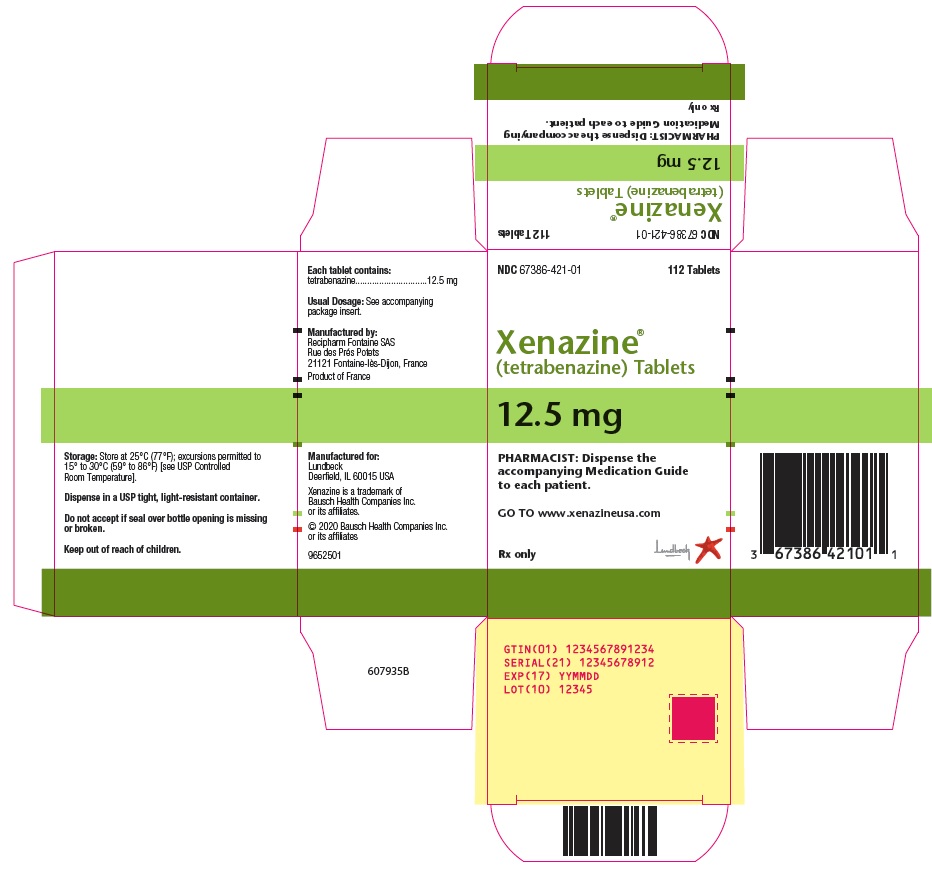
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 12.5 mg Carton
- NDC 67386-421-01
112 Tablets
Xenazine®
(tetrabenazine) Tablets - 12.5 mg
- PHARMACIST: Dispense the
accompanying Medication Guide
to each patient.GO TO www.xenazineusa.comRx only
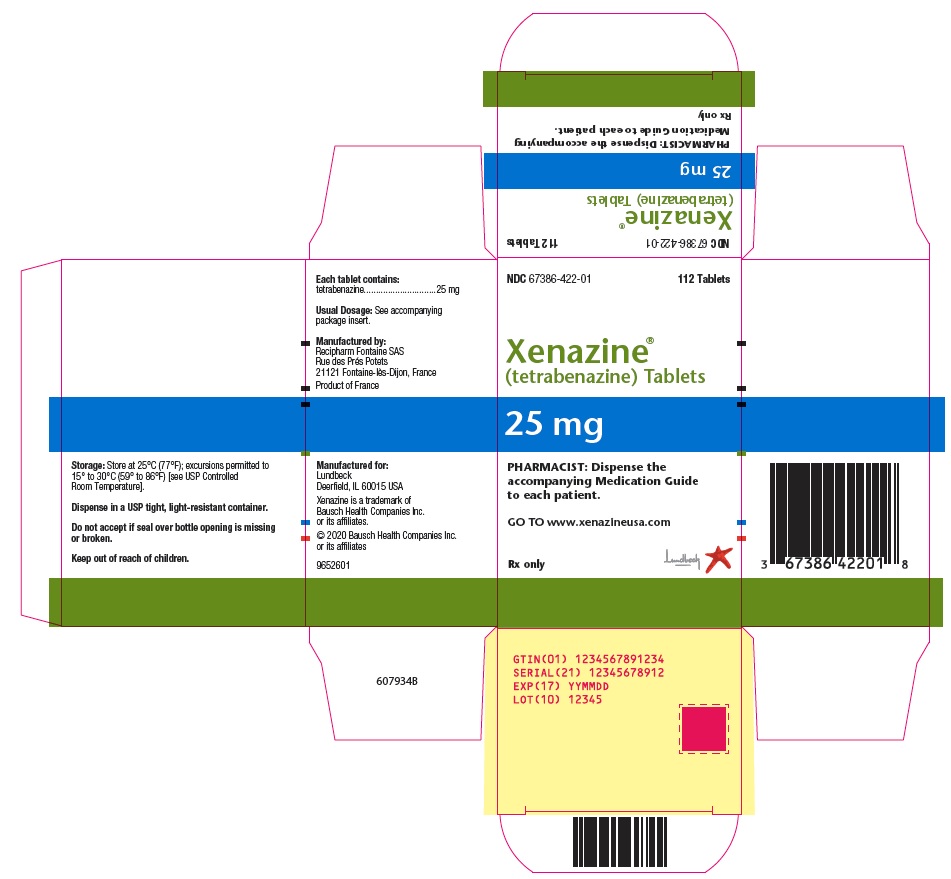
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 25 mg Carton
- NDC 67386-422-01112 TabletsXenazine® (tetrabenazine) Tablets 25 mg
- PHARMACIST: Dispense the
accompanying Medication Guide
to each patient.GO TO www.xenazineusa.comRx only
SRC: NLM .

