Niraparib
Generic name: niraparib
Brand name: Zejula
Dosage form: oral capsule (100 mg)
Drug class: PARP inhibitors
Medically reviewed by A Ras MD.
What is niraparib?
Niraparib is a prescription medicine that is used to treat ovarian, fallopian tube, or peritoneal cancer.
Description
Niraparib is an orally available poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor.
The chemical name for niraparib tosylate monohydrate is 2-{4-[(3S)-piperidin-3-yl]phenyl}-2H-indazole 7-carboxamide 4-methylbenzenesulfonate hydrate (1:1:1). The molecular formula is C26H30N4O5S and it has a molecular weight of 510.61 amu. The molecular structure is shown below:
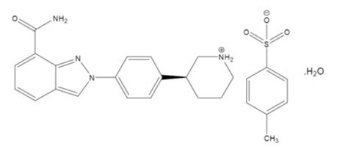
Niraparib tosylate monohydrate is a white to off-white, non-hygroscopic crystalline solid. Niraparib solubility is pH independent below the pKa of 9.95, with an aqueous free base solubility of 0.7 mg/mL to 1.1 mg/mL across the physiological pH range.
Each ZEJULA capsule contains 159.4 mg niraparib tosylate monohydrate equivalent to 100 mg niraparib free base as the active ingredient. The inactive ingredients in the capsule fill are magnesium stearate and lactose monohydrate. The capsule shell consists of titanium dioxide and gelatin in the white capsule body and FD&C Blue No. 1, FD&C Red No. 3, FD&C Yellow No. 5 (tartrazine), and gelatin in the purple capsule cap. The black printing ink consists of shellac, dehydrated alcohol, isopropyl alcohol, butyl alcohol, propylene glycol, purified water, strong ammonia solution, potassium hydroxide, and black iron oxide. The white printing ink consists of shellac, dehydrated alcohol, isopropyl alcohol, butyl alcohol, propylene glycol, sodium hydroxide, povidone, and titanium dioxide.
Mechanism of Action
Niraparib is an inhibitor of PARP enzymes, including PARP-1 and PARP-2, that play a role in DNA repair. In vitro studies have shown that niraparib-induced cytotoxicity may involve inhibition of PARP enzymatic activity and increased formation of PARP-DNA complexes resulting in DNA damage, apoptosis, and cell death. Increased niraparib‑induced cytotoxicity was observed in tumor cell lines with or without deficiencies in BRCA1/2. Niraparib decreased tumor growth in mouse xenograft models of human cancer cell lines with deficiencies in BRCA1/2 and in human patient‑derived xenograft tumor models with HRD that had either mutated or wild-type BRCA1/2.
Before taking niraparib, tell your doctor:
- If you are allergic to niraparib; any part of this medicine; or any other drugs, foods, or substances. Tell your doctor about the allergy and what signs you had.
- If you are breast-feeding. Do not breast-feed while you take niraparib or for 1 month after you stop niraparib.
This medicine may interact with other drugs or health problems.
Tell your doctor and pharmacist about all of your drugs (prescription or OTC, natural products, vitamins) and health problems. You must check to make sure that it is safe for you to take niraparib with all of your drugs and health problems. Do not start, stop, or change the dose of any drug without checking with your doctor.
What are some things I need to know or do while I take niraparib?
- Tell all of your health care providers that you take niraparib. This includes your doctors, nurses, pharmacists, and dentists.
- Rarely, a bone marrow problem called myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) and a type of leukemia have happened in patients treated with niraparib. Sometimes, this has been deadly.
- This medicine may lower the ability of the bone marrow to make blood cells that the body needs. If blood cell counts get very low, this can lead to bleeding problems, infections, or anemia. If you have questions, talk with the doctor.
- You may have more chance of getting an infection. Wash hands often. Stay away from people with infections, colds, or flu.
- You may bleed more easily. Be careful and avoid injury. Use a soft toothbrush and an electric razor.
- Have blood work checked as you have been told by the doctor. Talk with the doctor.
- This medicine may cause high blood pressure.
- Check blood pressure and heart rate as the doctor has told you.
- This medicine may affect being able to father a child. Talk with the doctor.
- This medicine may cause harm to an unborn baby. A pregnancy test will be done before you start niraparib to show that you are NOT pregnant.
- Women must use birth control while taking niraparib and for some time after the last dose. Ask your doctor how long to use birth control. If you get pregnant, call your doctor right away.
How is niraparib best taken?
Use niraparib as ordered by your doctor. Read all information given to you. Follow all instructions closely.
- Take niraparib at the same time of day.
- Take with or without food.
- Swallow whole. Do not chew, open, or crush.
- Taking niraparib at bedtime may help prevent upset stomach.
- If you throw up after taking a dose, do not repeat the dose. Take your next dose at your normal time.
- Keep taking niraparib as you have been told by your doctor or other health care provider, even if you feel well.
What do I do if I miss a dose?
- Skip the missed dose and go back to your normal time.
- Do not take 2 doses at the same time or extra doses.
What are the side effects of niraparib that I need to call my doctor about immediately?
WARNING/CAUTION: Even though it may be rare, some people may have very bad and sometimes deadly side effects when taking a drug. Tell your doctor or get medical help right away if you have any of the following signs or symptoms that may be related to a very bad side effect:
- Signs of an allergic reaction, like rash; hives; itching; red, swollen, blistered, or peeling skin with or without fever; wheezing; tightness in the chest or throat; trouble breathing, swallowing, or talking; unusual hoarseness; or swelling of the mouth, face, lips, tongue, or throat.
- Signs of infection like fever, chills, very bad sore throat, ear or sinus pain, cough, more sputum or change in color of sputum, pain with passing urine, mouth sores, or wound that will not heal.
- Signs of a urinary tract infection (UTI) like blood in the urine, burning or pain when passing urine, feeling the need to pass urine often or right away, fever, lower stomach pain, or pelvic pain.
- Signs of bleeding like throwing up or coughing up blood; vomit that looks like coffee grounds; blood in the urine; black, red, or tarry stools; bleeding from the gums; abnormal vaginal bleeding; bruises without a cause or that get bigger; or bleeding you cannot stop.
- Signs of high blood pressure like very bad headache or dizziness, passing out, or change in eyesight.
- Signs of electrolyte problems like mood changes, confusion, muscle pain or weakness, a heartbeat that does not feel normal, seizures, not hungry, or very bad upset stomach or throwing up.
- Signs of kidney problems like unable to pass urine, change in how much urine is passed, blood in the urine, or a big weight gain.
- Weight loss.
- A heartbeat that does not feel normal.
- Swelling of belly.
- Shortness of breath.
What are some other side effects of niraparib?
All drugs may cause side effects. However, many people have no side effects or only have minor side effects. Call your doctor or get medical help if any of these side effects or any other side effects bother you or do not go away:
- Constipation, diarrhea, stomach pain, upset stomach, throwing up, or feeling less hungry.
- Heartburn.
- Mouth irritation or mouth sores.
- Dry mouth.
- Feeling dizzy, tired, or weak.
- Back, muscle, or joint pain.
- Headache.
- Change in taste.
- Trouble sleeping.
- Anxiety.
- Nose or throat irritation.
These are not all of the side effects that may occur. If you have questions about side effects, call your doctor. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects.
You may report side effects to the FDA at 1-800-332-1088. You may also report side effects at https://www.fda.gov/medwatch.
If overdose is suspected:
If you think there has been an overdose, call your poison control center or get medical care right away. Be ready to tell or show what was taken, how much, and when it happened.
How do I store and/or throw out niraparib?
- Store at room temperature in a dry place. Do not store in a bathroom.
- Keep all drugs in a safe place. Keep all drugs out of the reach of children and pets.
- Throw away unused or expired drugs. Do not flush down a toilet or pour down a drain unless you are told to do so. Check with your pharmacist if you have questions about the best way to throw out drugs. There may be drug take-back programs in your area.
Label
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
- NDC 69656-103-30
- Zejula
- (niraparib)
- capsules
- 100 mg
- Rx only
- 30 capsules
- Each 100-mg capsule is equivalent to 159.4 mg of niraparib tosylate monohydrate.
- Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions are permitted between 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F), [See USP Controlled Room Temperature]
- Do not accept if membrane seal under cap is missing or broken.
- See prescribing information for dosage information.
- Keep out of reach of children.
- Contains FD&C Yellow No. 5 (tartrazine) as a color additive.
- Trademarks are owned by or licensed to the GSK group of companies.
- GlaxoSmithKline
- Research Triangle Park, NC 27709
- ©2021 GSK group of companies or its licensor.
- Rev.6/21
- 126929

SRC: NLM .