Neurontin
Generic name: gabapentin
Drug class: Gamma-aminobutyric acid analogs
Medically reviewed by A Ras MD.
What is Neurontin?
Neurontin is a prescription medicine used to treat pain from damaged nerves (postherpetic pain) that follows healing of shingles (a painful rash that comes after a herpes zoster infection) in adults.
It is also used to treat partial seizures when taken together with other medicines in adults and children 3 years of age and older with seizures.
Description
The active ingredient in NEURONTIN capsules, tablets, and oral solution is gabapentin, which has the chemical name 1-(aminomethyl)cyclohexaneacetic acid.
The molecular formula of gabapentin is C9H17NO2 and the molecular weight is 171.24. The structural formula of gabapentin is:
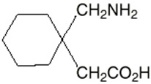
Gabapentin is a white to off-white crystalline solid with a pKa1 of 3.7 and a pKa2 of 10.7. It is freely soluble in water and both basic and acidic aqueous solutions. The log of the partition coefficient (n-octanol/0.05M phosphate buffer) at pH 7.4 is –1.25.
Each NEURONTIN capsule contains 100 mg, 300 mg, or 400 mg of gabapentin and the following inactive ingredients: lactose, cornstarch, talc, gelatin, titanium dioxide, FD&C Blue No. 2, yellow iron oxide (300 mg and 400 mg only), and red iron oxide (400 mg only).
Each NEURONTIN tablet contains 600 mg or 800 mg of gabapentin and the following inactive ingredients: poloxamer 407, copovidone, cornstarch, magnesium stearate, hydroxypropyl cellulose, talc, and candelilla wax
NEURONTIN oral solution contains 250 mg of gabapentin per 5 mL (50 mg per mL) and the following inactive ingredients: glycerin, xylitol, purified water, and artificial cool strawberry anise flavor.
Mechanism of Action
The precise mechanisms by which gabapentin produces its analgesic and antiepileptic actions are unknown. Gabapentin is structurally related to the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) but has no effect on GABA binding, uptake, or degradation. In vitro studies have shown that gabapentin binds with high-affinity to the α2δ subunit of voltage-activated calcium channels; however, the relationship of this binding to the therapeutic effects of gabapentin is unknown.
What is the most important information I should know about Neurontin?
Do not stop taking Neurontin without first talking to your healthcare provider.
Stopping Neurontin suddenly can cause serious problems.
Neurontin can cause serious side effects including:
1. Suicidal thoughts. Like other antiepileptic drugs, Neurontin may cause suicidal thoughts or actions in a very small number of people, about 1 in 500.
Call a healthcare provider right away if you have any of these symptoms, especially if they are new, worse, or worry you:
- thoughts about suicide or dying
- attempts to commit suicide
- new or worse depression
- new or worse anxiety
- feeling agitated or restless
- panic attacks
- trouble sleeping (insomnia)
- new or worse irritability
- acting aggressive, being angry, or violent
- acting on dangerous impulses
- an extreme increase in activity and talking (mania)
- other unusual changes in behavior or mood
How can I watch for early symptoms of suicidal thoughts and actions?
- Pay attention to any changes, especially sudden changes, in mood, behaviors, thoughts, or feelings.
- Keep all follow-up visits with your healthcare provider as scheduled.
Call your healthcare provider between visits as needed, especially if you are worried about symptoms.
Do not stop taking Neurontin without first talking to a healthcare provider.
- Stopping Neurontin suddenly can cause serious problems. Stopping a seizure medicine suddenly in a patient who has epilepsy can cause seizures that will not stop (status epilepticus).
- Suicidal thoughts or actions can be caused by things other than medicines. If you have suicidal thoughts or actions, your healthcare provider may check for other causes.
2. Changes in behavior and thinking. Using Neurontin in children 3 to 12 years of age can cause emotional changes, aggressive behavior, problems with concentration, restlessness, changes in school performance, and hyperactivity.
3. Neurontin may cause serious or life-threatening allergic reactions that may affect your skin or other parts of your body such as your liver or blood cells. This may cause you to be hospitalized or to stop Neurontin. You may or may not have a rash with an allergic reaction caused by Neurontin. Call a healthcare provider right away if you have any of the following symptoms:
- skin rash
- hives
- difficulty breathing
- fever
- swollen glands that do not go away
- swelling of your face, lips, throat, or tongue
- yellowing of your skin or of the whites of the eyes
- unusual bruising or bleeding
- severe fatigue or weakness
- unexpected muscle pain
- frequent infections
These symptoms may be the first signs of a serious reaction. A healthcare provider should examine you to decide if you should continue taking Neurontin.
4. Serious breathing problems. Serious breathing problems can occur when Neurontin is taken with other medicines that can cause severe sleepiness or decreased awareness, or when it is taken by someone who already has breathing problems. Watch for increased sleepiness or decreased breathing when starting Neurontin or when the dose is increased. Get help right away if breathing problems occur.
Who should not take Neurontin?
Do not take Neurontin if you are allergic to gabapentin or any of the other ingredients in Neurontin. See the end of this Medication Guide for a complete list of ingredients in Neurontin.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking Neurontin?
Before taking Neurontin, tell your healthcare provider if you:
- have or have had kidney problems or are on hemodialysis
- have or have had depression, mood problems, or suicidal thoughts or behavior
- have diabetes
- have breathing problems
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if Neurontin can harm your unborn baby. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you become pregnant while taking Neurontin. You and your healthcare provider will decide if you should take Neurontin while you are pregnant.
- Pregnancy Registry: If you become pregnant while taking Neurontin, talk to your healthcare provider about registering with the North American Antiepileptic Drug (NAAED) Pregnancy Registry. The purpose of this registry is to collect information about the safety of antiepileptic drugs during pregnancy. You can enroll in this registry by calling 1-888-233-2334.
- are breast-feeding or plan to breast-feed. Neurontin can pass into breast milk. You and your healthcare provider should decide how you will feed your baby while you take Neurontin.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Especially tell your healthcare provider if you take any opioid pain medicine (such as oxycodone), any medicines for anxiety (such as lorazepam) or insomnia (such as zolpidem), or any medicines that make you sleepy.
You may have a higher chance for dizziness, sleepiness, or breathing problems if these medicines are taken with Neurontin.
Taking Neurontin with certain other medicines can cause side effects or affect how well they work. Do not start or stop other medicines without talking to your healthcare provider.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them and show it to your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I take Neurontin?
- Take Neurontin exactly as prescribed. Your healthcare provider will tell you how much Neurontin to take.
- Do not change your dose of Neurontin without talking to your healthcare provider.
- If you take Neurontin tablets and break a tablet in half, the unused half of the tablet should be taken at your next scheduled dose. Half tablets not used within 28 days of breaking should be thrown away.
- Take Neurontin capsules with water.
- Neurontin tablets can be taken with or without food. If you take an antacid containing aluminum and magnesium, such as Maalox, Mylanta, Gelusil, Gaviscon, or Di-Gel, you should wait at least 2 hours before taking your next dose of Neurontin.
If you take too much Neurontin, call your healthcare provider or your local Poison Control Center right away at 1-800-222-1222.
What should I avoid while taking Neurontin?
- Do not drink alcohol or take other medicines that make you sleepy or dizzy while taking Neurontin without first talking with your healthcare provider. Taking Neurontin with alcohol or drugs that cause sleepiness or dizziness may make your sleepiness or dizziness worse.
- Do not drive, operate heavy machinery, or do other dangerous activities until you know how Neurontin affects you. Neurontin can slow your thinking and motor skills.
What are the possible side effects of Neurontin?
Neurontin may cause serious side effects including:
- see “What is the most important information I should know about Neurontin?”
- problems driving while using Neurontin. See “What I should avoid while taking Neurontin?”
- sleepiness and dizziness, which could increase the occurrence of accidental injury, including falls
- The most common side effects of Neurontin include:
- lack of coordination
- viral infection
- feeling drowsy
- nausea and vomiting
- difficulty with speaking
- tremor
- swelling, usually of legs and feet
- feeling tired
- fever
- jerky movements
- difficulty with coordination
- double vision
- unusual eye movement
Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all the possible side effects of Neurontin. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
Label
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 100 MG CAPSULE BOTTLE LABEL
ALWAYS DISPENSE WITH MEDICATION GUIDE
Pfizer
NDC 0071-0803-24
Neurontin®
(gabapentin) capsules
100 mg
100 Capsules
Rx only


ALWAYS DISPENSE WITH MEDICATION GUIDE
Pfizer
NDC 0071-0805-24
Neurontin®
(gabapentin) capsules
300 mg
100 Capsules
Rx only

ALWAYS DISPENSE WITH MEDICATION GUIDE
Pfizer
NDC 0071-0806-24
Neurontin®
(gabapentin) capsules
400 mg
100 Capsules
Rx only


Drug Interactions
A total of 264 medications are known to interact with Neurontin. Use the Interactions Checker Tool.
Common Interactions Checks
- Cymbalta
- Flexeril
- Klonopin
- lisinopril
- metformin
- omeprazole
- Synthroid
- tramadol
- trazodone
- Vitamin D3
- Xanax
General information about the safe and effective use of Neurontin
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use Neurontin for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Neurontin to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them.
This Medication Guide summarizes the most important information about Neurontin. If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about Neurontin that was written for healthcare professionals.
For more information go to http://www.pfizer.com or call 1-800-438-1985.
How should I store Neurontin?
- Store Neurontin capsules and tablets between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- Store Neurontin oral solution in the refrigerator between 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C).
Keep Neurontin and all medicines out of the reach of children.
What are the ingredients in Neurontin?
Active ingredient: gabapentin
Inactive ingredients:
Capsules: lactose, cornstarch, talc, gelatin, titanium dioxide and FD&C Blue No. 2.
300-mg capsule shell also contains: yellow iron oxide.
400-mg capsule shell also contains: red iron oxide, and yellow iron oxide.
Tablets: poloxamer 407, copovidone, cornstarch, magnesium stearate, hydroxypropyl cellulose, talc, and candelilla wax
SRC: NLM .