Qsymia
Generic name: phentermine and topiramate
Drug class: Anorexiants
Medically reviewed by A Ras MD.
What is Qsymia?
Qsymia is a prescription medicine that contains phentermine and topiramate extended-release that may help some obese adults or some overweight adults who also have weight-related medical problems lose weight and keep the weight off.
Qsymia should be used with a reduced calorie diet and increased physical activity.
It is not known if Qsymia changes your risk of heart problems or stroke or of death due to heart problems or stroke.
It is not known if Qsymia is safe and effective when taken with other prescription, over-the-counter, or herbal weight loss products.
It is not known if Qsymia is safe and effective in children under 18 years old
Qsymia is a federally controlled substance (CIV) because it contains phentermine and can be abused or lead to drug dependence. Keep Qsymia in a safe place, to protect it from theft. Never give your Qsymia to anyone else, because it may cause death or harm them. Selling or giving away this medicine is against the law.
Description
Qsymia capsule is a combination oral product comprised of immediate-release phentermine hydrochloride (expressed as the weight of the free base) and extended-release topiramate. Qsymia contains phentermine hydrochloride, a sympathomimetic amine anorectic, and topiramate, a sulfamate-substituted monosaccharide related to fructose antiepileptic drug.
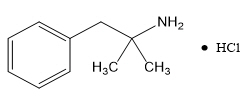
Phentermine Hydrochloride
The chemical name of phentermine hydrochloride is α,α-dimethylphenethylamine hydrochloride. The molecular formula is C 10H 15N • HCl and its molecular weight is 185.7 (hydrochloride salt) or 149.2 (free base). Phentermine hydrochloride is a white, odorless, hygroscopic, crystalline powder that is soluble in water, methanol, and ethanol. Its structural formula is:
Topiramate
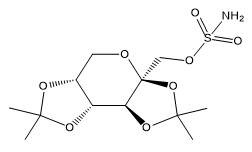
Topiramate is 2,3:4,5-di-O-isopropylidene-β-D-fructopyranose sulfamate. The molecular formula is C 12H 21NO 8S and its molecular weight is 339.4. Topiramate is a white to off-white crystalline powder with a bitter taste. It is freely soluble in methanol and acetone, sparingly soluble in pH 9 to pH 12 aqueous solutions and slightly soluble in pH 1 to pH 8 aqueous solutions. Its structural formula is:
Qsymia
Qsymia is available in four dosage strengths:
- Qsymia 3.75 mg/23 mg (phentermine 3.75 mg and topiramate 23 mg extended-release) capsules;
- Qsymia 7.5 mg/46 mg (phentermine 7.5 mg and topiramate 46 mg extended-release) capsules;
- Qsymia 11.25 mg/69 mg (phentermine 11.25 mg and topiramate 69 mg extended-release) capsules;
- Qsymia 15 mg/92 mg (phentermine 15 mg and topiramate 92 mg extended-release) capsules.
Each capsule contains the following inactive ingredients: methylcellulose, sucrose, starch, microcrystalline cellulose, ethylcellulose, povidone, gelatin, talc, titanium dioxide, FD&C Blue #1, FD&C Red #3, FD&C Yellow #5 and #6, and pharmaceutical black and white inks.
Mechanism of Action
Phentermine is a sympathomimetic amine with pharmacologic activity similar to the prototype drugs of this class used in obesity, amphetamine (d- and d/l-amphetamine). Drugs of this class used in obesity are commonly known as “anorectics” or “anorexigenics.” The effect of phentermine on chronic weight management is likely mediated by release of catecholamines in the hypothalamus, resulting in reduced appetite and decreased food consumption, but other metabolic effects may also be involved. The exact mechanism of action is not known.
The precise mechanism of action of topiramate on chronic weight management is not known. Topiramate’s effect on chronic weight management may be due to its effects on both appetite suppression and satiety enhancement, induced by a combination of pharmacologic effects including augmenting the activity of the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyrate, modulation of voltage-gated ion channels, inhibition of AMPA/kainite excitatory glutamate receptors, or inhibition of carbonic anhydrase.
What is the most important information I should know about Qsymia?
(For other side effects, also see “What are the possible side effects of Qsymia?”)
Qsymia can cause serious side effects, including:
- Birth defects (cleft lip/cleft palate). If you take Qsymia during pregnancy, your baby has a higher risk for birth defects called cleft lip and cleft palate. These defects can begin early in pregnancy, even before you know you are pregnant. Women who are pregnant must not take Qsymia. Women who can become pregnant should:
- Have a negative pregnancy test before taking Qsymia and every month while taking Qsymia.
- Use effective birth control (contraception) consistently while taking Qsymia. Talk to your healthcare provider about how to prevent pregnancy.
If you become pregnant while taking Qsymia, stop taking Qsymia immediately, and tell your healthcare provider right away. Healthcare providers and patients should report all cases of pregnancy to: FDA MedWatch at 1-800-FDA-1088, and The Qsymia Pregnancy Surveillance Program at 1-888-998-4887.
- Increases in heart rate. Qsymia can increase your heart rate at rest. Your healthcare provider should check your heart rate while you take Qsymia. Tell your healthcare provider if you experience, while at rest, a racing or pounding feeling in your chest lasting several minutes when taking Qsymia.
- Suicidal thoughts or actions. Topiramate, an ingredient in Qsymia, may cause you to have suicidal thoughts or actions. Call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of these symptoms, especially if they are new, worse, or worry you:
- thoughts about suicide or dying
- attempts to commit suicide
- new or worse depression
- new or worse anxiety
- feeling agitated or restless
- panic attacks
- trouble sleeping (insomnia)
- new or worse irritability
- acting aggressive, being angry, or violent
- acting on dangerous impulses
- an extreme increase in activity and talking (mania)
- other unusual changes in behavior or mood
- Serious eye problems which include:
- any sudden decrease in vision, with or without eye pain and redness,
- a blockage of fluid in the eye causing increased pressure in the eye (secondary angle closure glaucoma).
These problems can lead to permanent vision loss if not treated. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have any new eye symptoms.
Who should not take Qsymia?
Do not take Qsymia if you:
- are pregnant, planning to become pregnant, or become pregnant during Qsymia treatment.
- have glaucoma
- have thyroid problems (hyperthyroidism)
- are taking certain medicines called monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) or have taken MAOIs in the past 14 days.
- are allergic to topiramate, sympathomimetic amines such as phentermine, or any of the ingredients in Qsymia. See the end of this Medication Guide for a complete list of ingredients in Qsymia.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking Qsymia?
Tell your healthcare provider if you:
- are pregnant or planning to become pregnant
- have had a heart attack or stroke
- have or have had an abnormal heart rhythm
- have or have had depression, mood problems, or suicidal thoughts or behavior
- have eye problems, especially glaucoma
- have a history of metabolic acidosis (too much acid in the blood) or a condition that puts you at higher risk for metabolic acidosis such as:
- chronic diarrhea
- surgery
- a diet high in fat and low in carbohydrates (ketogenic diet)
- weak, brittle, or soft bones (osteomalacia, osteoporosis, osteopenia)
- decreased bone density
- have kidney problems, have kidney stones, or are getting kidney dialysis
- have liver problems
- have seizures or convulsions (epilepsy)
- are breastfeeding. It is not known if Qsymia passes into your breast milk. You and your healthcare provider should decide if you will take Qsymia or breastfeed. You should not do both.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and non-prescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Qsymia taken with other medicines may affect how each medicine works and may cause side effects.
Especially tell your healthcare provider if you take:
- Birth control pills. Tell your healthcare provider if your menstrual bleeding changes while you are taking birth control pills and Qsymia.
- Water pills (diuretics) such as hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ)
- Any medicines that impair or decrease your thinking, concentration, or muscle coordination
- Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors [such as zonegran (zonisamide), diamox (acetazolamide) or neptazane (methazolamide)]
- Seizure medicines such as Valproic acid (Depakene or Depakote )
Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for a list of these medicines, if you are not sure.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your healthcare provider and pharmacist each time you get a new medicine. Do not start a new medicine without talking to your healthcare provider.
How should I take Qsymia?
- Your healthcare provider should start you on a diet and exercise program when you start taking Qsymia. Stay on this program while you are taking Qsymia.
- Do not change your dose without talking to your healthcare provider.
- Qsymia can be taken with or without food.
- If you miss a dose of Qsymia, wait until the next morning to take your usual dose of Qsymia. Do not double your dose.
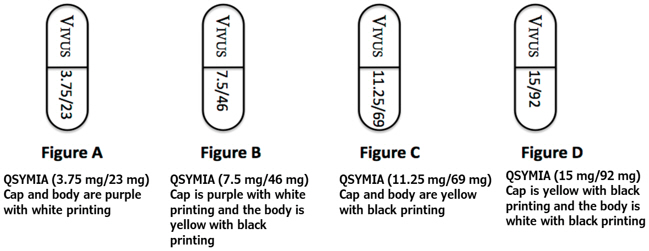
- To start treatment with Qsymia
- Take one Qsymia 3.75 mg/23 mg capsule (Figure A) once each morning for the first 14 days
- After taking Qsymia 3.75 mg/23 mg capsule for 14 days, then take one Qsymia 7.5 mg/46 mg capsule (Figure B) once each morning
- After taking Qsymia for 12 weeks
- Your healthcare provider should either (1) tell you to stop taking Qsymia or (2) increase your dose of Qsymia if you do not lose a certain amount of weight within the first 12 weeks of treatment at the recommended dose.
- If your healthcare provider increases the dose of Qsymia
- Take one Qsymia 11.25 mg/69 mg capsule (Figure C) once each morning for 14 days
- After taking 14 days of Qsymia 11.25 mg/69 mg capsule, then take one Qsymia 15 mg/92 mg capsule (Figure D) once each morning
- Stopping Qsymia treatment
Your healthcare provider should tell you to stop taking Qsymia if you have not lost a certain amount of weight after an additional 12 weeks of treatment on the higher dose.
Do not stop taking Qsymia without talking to your healthcare provider. Stopping Qsymia suddenly can cause serious problems, such as seizures. Your healthcare provider will tell you how to stop taking Qsymia slowly.

If you take too much Qsymia, call your healthcare provider or go to the nearest emergency room right away.
What should I avoid while taking Qsymia?
- Do not get pregnant while taking Qsymia. See “What is the most important information i should know about Qsymia?”
- Do not drink alcohol while taking Qsymia. Qsymia and alcohol can affect each other causing side effects such as sleepiness or dizziness.
- Do not drive a car or operate heavy machinery, or do other dangerous activities until you know how Qsymia affects you. Qsymia can slow your thinking and motor skills, and may affect vision.
What are the possible side effects of Qsymia?
- See “What is the most important information I should know about Qsymia?” at the beginning of this Medication Guide
- Mood changes and trouble sleeping. Qsymia may cause depression or mood problems, and trouble sleeping. Tell your healthcare provider if symptoms occur.
- Concentration, memory, and speech difficulties. Qsymia may affect how you think and cause confusion, problems with concentration, attention, memory, or speech. Tell your healthcare provider if symptoms occur.
- Increases of acid in bloodstream (metabolic acidosis). If left untreated, metabolic acidosis can cause brittle or soft bones (osteoporosis, osteomalacia, osteopenia), kidney stones, can slow the rate of growth in children, and may possibly harm your baby if you are pregnant. Metabolic acidosis can happen with or without symptoms. Sometimes people with metabolic acidosis will:
- feel tired
- not feel hungry (loss of appetite)
- feel changes in heartbeat
- have trouble thinking clearly
- Your healthcare provider should do a blood test to measure the level of acid in your blood before and during your treatment with Qsymia.
- Low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus who also take medicines used to treat type 2 diabetes mellitus. Weight loss can cause low blood sugar in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus who also take medicines used to treat type 2 diabetes mellitus (such as insulin or sulfonylureas). You should check your blood sugar before you start taking Qsymia and while you take Qsymia.
- Possible seizures if you stop taking Qsymia too fast. Seizures may happen in people who may or may not have had seizures in the past if you stop Qsymia too fast. Your healthcare provider will tell you how to stop taking Qsymia slowly.
- Kidney stones. Drinking plenty of fluids when taking Qsymia to help decrease your chances of getting kidney stones. If you get severe side or back pain, and/or blood in your urine, call your healthcare provider
- Decreased sweating and increased body temperature (fever). People should be watched for signs of decreased sweating and fever, especially in hot temperatures. Some people may need to be hospitalized for this condition.
Common side effects of Qsymia include:
- numbness or tingling in the hands, arms, feet, or face (paraesthesia)
- dizziness
- change in the way foods taste or loss of taste (dysgeusia)
- trouble sleeping (insomnia)
- constipation
- dry mouth
Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or does not go away.
These are not all of the possible side effects of Qsymia. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to VIVUS at 1-888-998-4887 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
General information about the safe and effective use of Qsymia
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use Qsymia for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Qsymia to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them.
This Medication Guide summarizes important information about Qsymia. If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about Qsymia that is written for healthcare professionals.
For more information, go to www.QsymiaREMS.com or call 1-888-998-4887.
How should I store Qsymia?
- Store Qsymia at room temperature between 59°F to 77°F (15°C to 25°C).
Keep Qsymia and all medicines out of the reach of children.
What are the ingredients in Qsymia?
Active Ingredient: phentermine hydrochloride and topiramate
Inactive Ingredients: methylcellulose, sucrose, starch, microcrystalline cellulose, ethylcellulose, povidone, gelatin, talc, titanium dioxide, FD&C Blue #1, FD&C Red #3, FD&C Yellow #5 and #6, and pharmaceutical black and white inks.
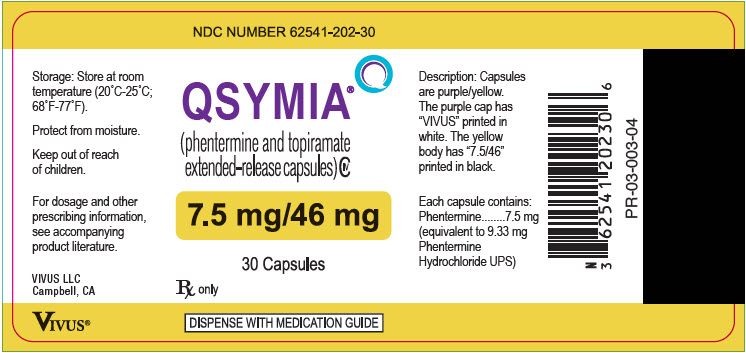
Label
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 7.5 MG/46 MG CAPSULE BOTTLE LABEL
- NDC NUMBER 62541-202-30
- Qsymia ®
(phentermine and topiramate
extended-release) capsules CIV - 7.5 mg/46 mg
- 30 Capsules
- Rx only
- DISPENSE WITH MEDICATION GUIDE
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 3.75 MG/23 MG CAPSULE BOTTLE LABEL
- NDC NUMBER 62541-201-30
- Qsymia ®
(phentermine and topiramate
extended-release) capsules CIV - 3.75 mg/23 mg
- 30 Capsules
- Rx only
- DISPENSE WITH MEDICATION GUIDE
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 11.25 MG/69 MG CAPSULE BOTTLE LABEL
- NDC NUMBER 62541-203-30
- Qsymia ®
(phentermine and topiramate
extended-release) capsules CIV - 11.25 mg/69 mg
- 30 Capsules
- Rx only
- DISPENSE WITH MEDICATION GUIDE

SRC: NLM .

