Janumet
Generic name: metformin and sitagliptin
Brand names: Janumet, Janumet XR
Drug class: Antidiabetic combinations
Medically reviewed by A Ras MD.
What is Janumet?
Janumet is a prescription medicine that contains 2 prescription diabetes medicines, sitagliptin (Januvia) and metformin. Janumet can be used along with diet and exercise to lower blood sugar in adults with type 2 diabetes.
Janumet is not for people with type 1 diabetes.
If you have had pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas) in the past, it is not known if you have a higher chance of getting pancreatitis while you take Janumet.
The safety and effectiveness of Janumet have not been established in pediatric patients.
Description
JANUMET (sitagliptin and metformin HCl) tablets for oral use contain two antihyperglycemic drugs: sitagliptin and metformin HCl.
Sitagliptin
Sitagliptin is an orally-active inhibitor of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) enzyme. Sitagliptin is present in JANUMET tablets in the form of sitagliptin phosphate monohydrate. Sitagliptin phosphate monohydrate is described chemically as 7-[(3R)-3-amino-1-oxo-4-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)butyl]-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-3-(trifluoromethyl)-1,2,4-triazolo[4,3-a]pyrazine phosphate (1:1) monohydrate with an empirical formula of C16H15F6N5O∙H3PO4∙H2O and a molecular weight of 523.32. The structural formula is:
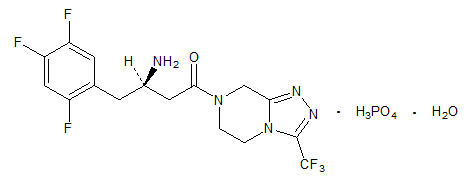
Sitagliptin phosphate monohydrate is a white to off-white, crystalline, non-hygroscopic powder. It is soluble in water and N,N-dimethyl formamide; slightly soluble in methanol; very slightly soluble in ethanol, acetone, and acetonitrile; and insoluble in isopropanol and isopropyl acetate.
Metformin HCl
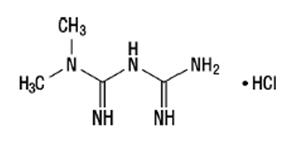
Metformin HCl (N,N-dimethylimidodicarbonimidic diamide hydrochloride) is not chemically or pharmacologically related to any other classes of oral antihyperglycemic agents. Metformin HCl is a white to off-white crystalline compound with a molecular formula of C4H11N5∙HCl and a molecular weight of 165.63. Metformin HCl is freely soluble in water and is practically insoluble in acetone, ether, and chloroform. The pKa of metformin HCl is 12.4. The pH of a 1% aqueous solution of metformin HCl is 6.68. The structural formula is as shown:
JANUMET
JANUMET is available as film-coated tablets containing:
- 64.25 mg sitagliptin monohydrate equivalent to 50 mg of sitagliptin and 389.93 mg of metformin equivalent to 500 mg metformin HCl (JANUMET 50/500).
- 64.25 mg sitagliptin monohydrate equivalent to 50 mg of sitagliptin and 779.86 mg of metformin equivalent to 1000 mg metformin HCl (JANUMET 50/1000).
Each film-coated tablet of JANUMET contains the following inactive ingredients: microcrystalline cellulose, polyvinylpyrrolidone, sodium lauryl sulfate, and sodium stearyl fumarate. In addition, the film coating contains the following inactive ingredients: polyvinyl alcohol, polyethylene glycol, talc, titanium dioxide, red iron oxide, and black iron oxide.
Mechanism of Action
JANUMET
JANUMET combines two antihyperglycemic agents with complementary mechanisms of action to improve glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: sitagliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor, and metformin HCl, a member of the biguanide class.
Sitagliptin
Sitagliptin is a DPP-4 inhibitor, which is believed to exert its actions in patients with type 2 diabetes by slowing the inactivation of incretin hormones. Concentrations of the active intact hormones are increased by sitagliptin, thereby increasing and prolonging the action of these hormones. Incretin hormones, including glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP), are released by the intestine throughout the day, and levels are increased in response to a meal. These hormones are rapidly inactivated by the enzyme DPP-4. The incretins are part of an endogenous system involved in the physiologic regulation of glucose homeostasis. When blood glucose concentrations are normal or elevated, GLP-1 and GIP increase insulin synthesis and release from pancreatic beta cells by intracellular signaling pathways involving cyclic AMP. GLP-1 also lowers glucagon secretion from pancreatic alpha cells, leading to reduced hepatic glucose production. By increasing and prolonging active incretin levels, sitagliptin increases insulin release and decreases glucagon levels in the circulation in a glucose-dependent manner. Sitagliptin demonstrates selectivity for DPP-4 and does not inhibit DPP-8 or DPP-9 activity in vitro at concentrations approximating those from therapeutic doses.
Metformin
Metformin is an antihyperglycemic agent which improves glucose tolerance in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, lowering both basal and postprandial plasma glucose. Metformin decreases hepatic glucose production, decreases intestinal absorption of glucose, and improves insulin sensitivity by increasing peripheral glucose uptake and utilization. With metformin therapy, insulin secretion remains unchanged while fasting insulin levels and day-long plasma insulin response may decrease.
What is the most important information I should know about Janumet?
Janumet can cause serious side effects, including:
1. Lactic Acidosis. Metformin, one of the medicines in Janumet, can cause a rare but serious condition called lactic acidosis (a buildup of an acid in the blood) that can cause death. Lactic acidosis is a medical emergency and must be treated in the hospital.
Stop taking Janumet and call your doctor right away if you have any of the following symptoms, which could be signs of lactic acidosis:
- you feel cold in your hands or feet
- you feel dizzy or lightheaded
- you have a slow or irregular heartbeat
- you feel very weak or tired
- you have unusual (not normal) muscle pain
- you have trouble breathing
- you feel sleepy or drowsy
- you have stomach pains, nausea or vomiting
Most people who have had lactic acidosis with metformin have other things that, combined with the metformin, led to the lactic acidosis. Tell your doctor if you have any of the following, because you have a higher chance for getting lactic acidosis with Janumet if you:
- have severe kidney problems or your kidneys are affected by certain x-ray tests that use injectable dye
- have liver problems
- drink alcohol very often, or drink a lot of alcohol in short-term “binge” drinking
- get dehydrated (lose a large amount of body fluids). This can happen if you are sick with a fever, vomiting, or diarrhea. Dehydration can also happen when you sweat a lot with activity or exercise and do not drink enough fluids
- have surgery
- have a heart attack, severe infection, or stroke
- are 65 years of age or older
The best way to keep from having a problem with lactic acidosis from metformin is to tell your doctor if you have any of the problems in the list above. Your doctor may decide to stop your Janumet for a while if you have any of these things.
Janumet can have other serious side effects. See “What are the possible side effects of Janumet?” below.
2. Pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas) which may be severe and lead to death. Certain medical problems make you more likely to get pancreatitis.
Before you start taking Janumet tell your doctor if you have ever had:
- pancreatitis
- stones in your gallbladder (gallstones)
- a history of alcoholism
- high blood triglyceride levels
Stop taking Janumet and call your doctor right away if you have pain in your stomach area (abdomen) that is severe and will not go away. The pain may be felt going from your abdomen through to your back. The pain may happen with or without vomiting. These may be symptoms of pancreatitis.
3. Heart failure. Heart failure means that your heart does not pump blood well enough.
Before you start taking Janumet, tell your doctor if you have ever had heart failure or have problems with your kidneys.
Contact your healthcare provider right away if you have any of the following symptoms:
- increasing shortness of breath or trouble breathing, especially when you lie down
- swelling or fluid retention, especially in the feet, ankles or legs
- an unusually fast increase in weight
- unusual tiredness
These may be symptoms of heart failure.
Who should not take Janumet?
Do not take Janumet if:
- you have severe kidney problems.
- have diabetic ketoacidosis.
- you are allergic to any of the ingredients in Janumet. See the end of this Medication Guide for a complete list of ingredients in Janumet.
Symptoms of a serious allergic reaction to Janumet may include rash, raised red patches on your skin (hives) or swelling of the face, lips, tongue, and throat that may cause difficulty in breathing or swallowing.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking Janumet?
Before you take Janumet, tell your doctor about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- have or have had inflammation of your pancreas (pancreatitis).
- have kidney problems.
- have liver problems.
- have heart failure.
- drink alcohol very often or drink a lot of alcohol in short-term “binge” drinking.
- are going to get an injection of dye or contrast agents for an x-ray procedure. Janumet may need to be stopped for a short time. Talk to your healthcare provider about when you should stop Janumet and when you should start Janumet again. See “What is the most important information I should know about Janumet?”.
- have low levels of vitamin B12 in your blood.
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if Janumet will harm your unborn baby. If you are pregnant, talk with your doctor about the best way to control your blood sugar while you are pregnant.
Pregnancy Registry: If you take Janumet at any time during your pregnancy, talk with your doctor about how you can join the Janumet pregnancy registry. The purpose of this registry is to collect information about the health of you and your baby. You can enroll in this registry by calling 1-800-986-8999. - are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if Janumet will pass into your breast milk. Talk with your doctor about the best way to feed your baby if you are taking Janumet.
- are a woman who has not gone through menopause (premenopausal) who does not have periods regularly or at all. Janumet can cause the release of an egg from an ovary in a woman (ovulation). This can increase your chance of getting pregnant. Tell your doctor right away if you become pregnant while taking Janumet.
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Janumet may affect the way other medicines work and other medicines may affect how Janumet works.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of your medicines and show it to your doctor and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I take Janumet?
- Take Janumet exactly as your doctor tells you. Your doctor will tell you how many Janumet tablets to take and when you should take them.
- Ydoctor may change your dose of Janumet if needed.
- Your doctor may tell you to take Janumet along with certain other diabetes medicines. Low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) can happen more often when Janumet is taken with certain other diabetes medicines. See “What are the possible side effects of Janumet?”.
- Take Janumet with meals to help to lower your chance of having an upset stomach.
- Do not break or cut Janumet tablets before swallowing. If you cannot swallow Janumet tablets whole, tell your doctor.
- Continue to take Janumet as long as your doctor tells you.
- If you take too much Janumet, call your doctor or local Poison Control Center right away.
- If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. If you do not remember until it is time for your next dose, skip the missed dose and go back to your regular schedule. Do not take 2 doses of Janumet at the same time.
- You may need to stop taking Janumet for a short time. Call your doctor for instructions if you:
- are dehydrated (have lost too much body fluid). Dehydration can occur if you are sick with severe vomiting, diarrhea or fever, or if you drink a lot less fluid than normal.
- plan to have surgery.
- are going to get an injection of dye or contrast agent for an x-ray procedure. See “What is the most important information I should know about Janumet?” and “What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking Janumet?”.
- When your body is under some types of stress, such as fever, trauma (such as a car accident), infection or surgery, the amount of diabetes medicine that you need may change. Tell your doctor right away if you have any of these problems and follow your doctor’s instructions.
- Check your blood sugar as your doctor tells you to.
- Stay on your prescribed diet and exercise program while taking Janumet.
- Talk to your doctor about how to prevent, recognize and manage low blood sugar (hypoglycemia), high blood sugar (hyperglycemia), and problems you have because of your diabetes.
- Your doctor will check your diabetes with regular blood tests, including your blood sugar levels and your hemoglobin A1C.
- Your doctor will do blood tests to check how well your kidneys are working before and during your treatment with Janumet.
What are the possible side effects of Janumet?
Janumet may cause serious side effects, including:
- See “What is the most important information I should know about Janumet?”.
- Kidney problems, sometimes requiring dialysis.
- Low vitamin B12 (vitamin B12 deficiency). Using metformin for long periods of time may cause a decrease in the amount of vitamin B12 in your blood, especially if you have had low vitamin B12 blood levels before. Your doctor may do blood tests to check your vitamin B12 levels.
- Low blood sugar (hypoglycemia). If you take Janumet with another medicine that can cause low blood sugar, such as a sulfonylurea or insulin, your risk of getting low blood sugar is higher. The dose of your sulfonylurea medicine or insulin may need to be lowered while you use Janumet. Signs and symptoms of low blood sugar may include:
- headache
- drowsiness
- irritability
- hunger
- dizziness
- confusion
- sweating
- feeling jittery
- weakness
- fast heart beat
- Serious allergic reactions. If you have any symptoms of a serious allergic reaction, stop taking Janumet and call your doctor right away. See “Who should not take Janumet?”. Your doctor may give you a medicine for your allergic reaction and prescribe a different medicine for your diabetes.
- Joint pain. Some people who take medicines called DPP-4 inhibitors, one of the medicines in Janumet, may develop joint pain that can be severe. Call your doctor if you have severe joint pain.
- Skin reaction. Some people who take medicines called DPP-4 inhibitors, one of the medicines in Janumet, may develop a skin reaction called bullous pemphigoid that can require treatment in a hospital. Tell your doctor right away if you develop blisters or the breakdown of the outer layer of your skin (erosion). Your doctor may tell you to stop taking Janumet.
The most common side effects of Janumet include:
- stuffy or runny nose and sore throat
- gas, upset stomach, indigestion
- headache
- upper respiratory infection
- weakness
- diarrhea
- low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) when used in combination with certain medications, such as a sulfonylurea or insulin.
- nausea and vomiting
Taking Janumet with meals can help lessen the common stomach side effects of metformin that usually happen at the beginning of treatment. If you have unusual or sudden stomach problems, talk with your doctor. Stomach problems that start later during treatment may be a sign of something more serious.
Janumet may have other side effects, including swelling of the hands or legs. Swelling of the hands and legs can happen if you take Janumet in combination with rosiglitazone (Avandia). Rosiglitazone is another type of diabetes medicine.
Tell your doctor if you have any side effect that bothers you, is unusual, or does not go away.
These are not all the possible side effects of Janumet. For more information, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
General information about the safe and effective use of Janumet
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in Medication Guides. Do not use Janumet for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Janumet to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them.
This Medication Guide summarizes the most important information about Janumet. If you would like to know more information, talk with your doctor. You can ask your doctor or pharmacist for information about Janumet that is written for health professionals.
How should I store Janumet?
Store Janumet at 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
Keep Janumet and all medicines out of the reach of children.
What are the ingredients in Janumet?
Active ingredients: sitagliptin and metformin hydrochloride
Inactive ingredients: microcrystalline cellulose, polyvinylpyrrolidone, sodium lauryl sulfate, and sodium stearyl fumarate.
The tablet film coating contains the following inactive ingredients: polyvinyl alcohol, polyethylene glycol, talc, titanium dioxide, red iron oxide, and black iron oxide.
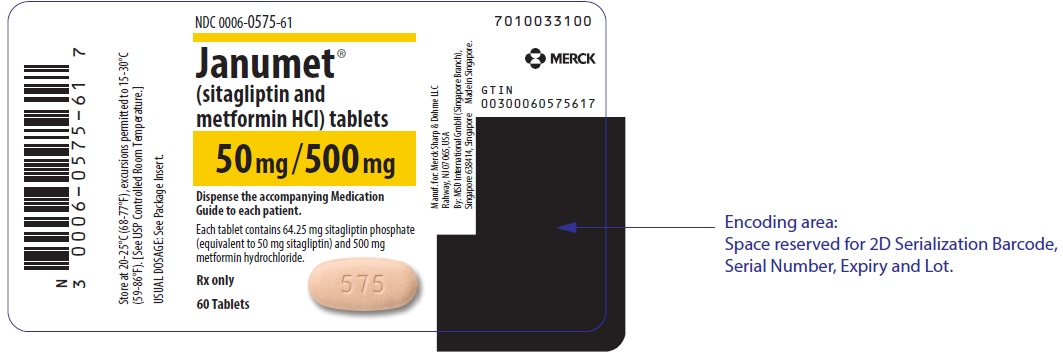
Label
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 50 MG/500 MG TABLET BOTTLE LABEL
- NDC 0006-0575-61
- Janumet®
(sitagliptin and
metformin HCl) tablets - 50 mg/500 mg
- Dispense the accompanying Medication
Guide to each patient. - Each tablet contains 64.25 mg sitagliptin phosphate
(equivalent to 50 mg sitagliptin) and 500 mg
metformin hydrochloride. - Rx only
- 60 Tablets

SRC: NLM .