Minocin
Generic name: Minocycline Injection
Drug class: Tetracyclines
Medically reviewed by A Ras MD.
What is Minocin?
Minocin is a tetracycline-class antibiotic medicine. Minocin is used to treat certain infections caused by bacteria. These include infections of the skin, respiratory tract, urinary tract, some sexually transmitted diseases, and others. Minocin may be used along with other treatments for severe acne.
Sometimes other germs, called viruses, cause infections. The common cold is a virus. Minocin, like other antibiotics, does not treat viruses.
Description
MINOCIN (minocycline) for Injection, is a sterile formulation of a semisynthetic derivative of tetracycline. The chemical name of minocycline is 4,7-Bis(dimethylamino)- 1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a-octahydro-3,10,12,12a- tetrahydroxy-1,11-dioxo-2- naphthacenecarboxamide monohydrochloride.
Its structural formula is:
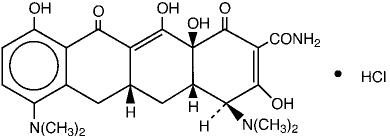 |
||
| C23H27N3O7∙HCl | M.W. 493.94 | |
MINOCIN is supplied as a sterile yellow to amber lyophilized powder for intravenous infusion. Each vial contains minocycline HCl equivalent to 100 mg minocycline, 269 mg magnesium sulfate heptahydrate (2.2 mEq of magnesium) (an inactive ingredient) and sodium hydroxide (to adjust pH). When reconstituted with 5 mL of Sterile Water for Injection USP the pH ranges from 4.5
Who should not take Minocin?
Do not take Minocin if you are allergic to minocycline or other tetracycline antibiotics.
Ask your doctor or pharmacist for a list of these medications if you are not sure. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in Minocin.
Minocin is not recommended for pregnant women or children up to 8 years old because:
- Minocin may harm an unborn baby
- Minocin may permanently turn a baby’s or child’s teeth yellow-gray-brown during tooth development. Tooth development happens in the last half of pregnancy and birth to age 8 years.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking Minocin?
Tell your doctor about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- have liver or kidney problems.
- are pregnant or planning to become pregnant. Minocin may harm your unborn baby. Stop taking Minocin and call your doctor if you become pregnant while taking it.
- are breast feeding. Minocin passes into your milk and may harm your baby. You should decide whether to use Minocin or breastfeed, but not both.
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you are taking including prescription and non-prescription medications, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Minocin and other medicines may interact. Especially tell your doctor if you take:
- birth control pills. Minocin may make your birth control pills less effective.
- a blood thinner medicine. The dose of your blood thinner may have to be lowered.
- a penicillin antibiotic medicine. Minocin and penicillins should not be used together.
- migraine medicines called ergot alkaloids.
- an acne medicine called isotretinoin (Accutane, Amnesteem, Claravis, Sotret).
- antacids that contain aluminum, calcium, or magnesium, or iron-containing products.
Know the medicines you take, keep a list of them to show your doctor and pharmacist each time you get a new medicine.
How should I take Minocin?
- Take Minocin capsules exactly as your doctor tells you to take them. Skipping doses may:
- Decrease the effectiveness of the treatment
- Increase the chance that bacteria will develop resistance to Minocin
- Take Minocin with a full glass of liquid. Taking Minocin with enough liquid may lower your chance of getting irritation or ulcers in your esophagus. Your esophagus is the tube that connects your mouth to your stomach.
- Minocin capsules may be taken with or without food. If you forget to take Minocin, take it as soon as you remember.
- If you take too much Minocin, call your doctor or poison control center right away.
What are the possible side effects of Minocin?
Minocin may cause serious side effects. Stop Minocin and call your doctor if you have:
- watery diarrhea
- bloody stools
- stomach cramps
- unusual headaches
- blurred vision
- fever
- rash
- joint pain
- feeling very tired
- swollen lymph nodes
Minocin may also cause:
- central nervous system effects. Symptoms include light-headedness, dizziness, and a spinning feeling (vertigo). You should not drive or operate machines if you have these symptoms.
- sun sensitivity (photosensitivity). You may get a worse sunburn with Minocin. Avoid sun exposure and the use of sunlamps or tanning beds. Protect your skin while out in the sunlight. Stop Minocin and call your doctor if your skin turns red.
These are not all the side effects with Minocin. Ask your doctor or pharmacist for more information.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to the FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
General information about the safe and effective use of Minocin
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use Minocin capsules for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Minocin capsules to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them.
This Patient Information leaflet summarizes the most important information about Minocin.
If you would like more information, talk with your doctor.
Your doctor or pharmacist can give you information about Minocin that is written for healthcare professionals. For more information, you can also call Valeant Pharmaceuticals North America LLC at 1-800-321-4576.
How should I store Minocin?
- Store Minocin capsules at room temperature and away from excess heat and moisture.
- Throw away any Minocin that is outdated or no longer needed.
- Keep Minocin capsules and all medicines out of the reach of children.
What are the ingredients in Minocin?
Active ingredient: minocycline hydrochloride, 50 mg and 100 mg
Inactive ingredients: FD&C Blue #1, gelatin, titanium dioxide and FD&C Yellow #10. The 50 mg capsule shell also contains black and yellow iron oxides.
Label
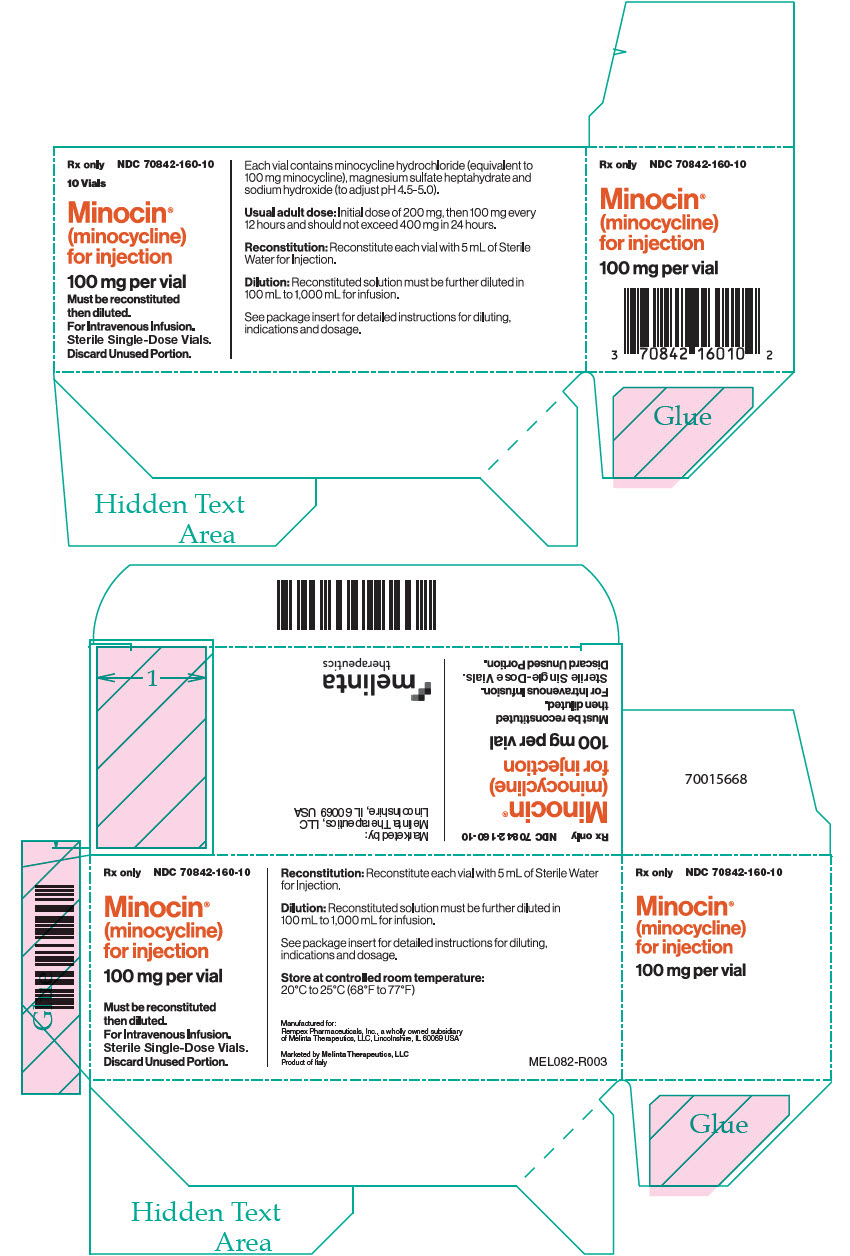
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 100 MG VIAL CARTON
- Rx only
NDC 70842-160-10 - 10 Vials
- Minocin®
(minocycline)
for injection - 100 mg per vial
- Must be reconstituted
then diluted.
For Intravenous Infusion.
Sterile Single-Dose Vials.
Discard Unused Portion. - Each vial contains minocycline hydrochloride (equivalent to
100 mg minocycline), magnesium sulfate heptahydrate and
sodium hydroxide (to adjust pH 4.5-5.0). - Usual adult dose: Initial dose of 200 mg, then 100 mg every
12 hours and should not exceed 400 mg in 24 hours. - Reconstitution: Reconstitute each vial with 5 mL of Sterile
Water for Injection. - Dilution: Reconstituted solution must be further diluted in
100 mL to 1,000 mL for infusion. - See package insert for detailed instructions for diluting,
indications and dosage.

SRC: NLM .