Nexavar
Generic name: sorafenib
Drug classes: Multikinase inhibitors, VEGF/VEGFR inhibitors
Medically reviewed by A Ras MD.
What is Nexavar?
Nexavar is a prescription medicine used to treat:
- a type of liver cancer called hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) that cannot be removed by surgery
- a type of kidney cancer called renal cell carcinoma (RCC)
- a type of thyroid cancer called differentiated thyroid carcinoma (DTC) that can no longer be treated with radioactive iodine and is progressing
It is not known if Nexavar is safe and effective in children.
Description
Sorafenib, a kinase inhibitor, is the tosylate salt of sorafenib. Sorafenib tosylate has the chemical name 4-(4-{3-[4-Chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ureido}phenoxy)N2-methylpyridine-2-carboxamide 4-methylbenzenesulfonate. The molecular formula of sorafenib tosylate is C21H16ClF3N4O3 x C7H8O3S and the molecular weight of sorafenib tosylate is 637.0 g/mole. Its structural formula is:
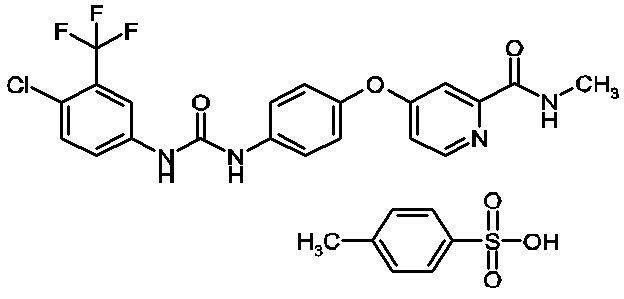
Sorafenib tosylate is a white to yellowish or brownish solid. Sorafenib tosylate is practically insoluble in aqueous media, slightly soluble in ethanol and soluble in PEG 400.
NEXAVAR (sorafenib), for oral use is supplied as film-coated tablets containing 200 mg sorafenib equivalent to 274 mg sorafenib tosylate and the following inactive ingredients: croscarmellose sodium, ferric oxide red, hypromellose, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene glycol sodium lauryl sulphate, and titanium dioxide.
Mechanism of Action
Sorafenib is a kinase inhibitor that decreases tumor cell proliferation in vitro. Sorafenib was shown to inhibit multiple intracellular (c-CRAF, BRAF and mutant BRAF) and cell surface kinases (KIT, FLT- 3, RET, RET/PTC, VEGFR-1, VEGFR- 2, VEGFR- 3, and PDGFR-ß). Several of these kinases are thought to be involved in tumor cell signaling, angiogenesis and apoptosis. Sorafenib inhibited tumor growth of HCC, RCC, and DTC human tumor xenografts in immunocompromised mice. Reductions in tumor angiogenesis were seen in models of HCC and RCC upon sorafenib treatment, and increases in tumor apoptosis were observed in models of HCC, RCC, and DTC.
Who should not take Nexavar?
Do not take Nexavar if you:
- are allergic to sorafenib or any of the other ingredients in Nexavar.See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in Nexavar.
- have squamous cell lung cancer and receive carboplatin and paclitaxel.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking Nexavar?
Before taking Nexavar, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions including if you:
- have heart problems including a condition called “congenital long QT syndrome”
- have chest pain
- have abnormal magnesium, potassium, or calcium blood levels
- have bleeding problems
- have high blood pressure
- plan to have surgery or have had a recent surgery. You should stop taking Nexavar at least 2 weeks before planned surgery. See “What are the possible side effects of Nexavar?
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. Nexavar may harm your unborn baby. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you become pregnant during treatment with Nexavar.
- For females who are able to become pregnant:
- Your healthcare should do a pregnancy test before you start treatment with Nexavar.
- Use effective birth control (contraception) during your treatment with Nexavar and for 6 months after the last dose of Nexavar.
- For males with female partners who are able to become pregnant:
- Use effective birth control (contraception) during your treatment with Nexavar and for 3 months after the last dose of Nexavar.
- For females who are able to become pregnant:
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if Nexavar passes into your breast milk. Do not breastfeed during treatment with Nexavar and for 2 weeks after receiving the last dose of Nexavar.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
Especially tell your healthcare provider if you take the medicine warfarin
How should I take Nexavar?
- Take Nexavar exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to take it.
- Take Nexavar 2 times a day. Your healthcare provider may change your dose, temporarily stop treatment or completely stop treatment with Nexavar if you have side effects.
- Take Nexavar without food (at least 1 hour before or 2 hours after a meal).
- If you miss a dose of Nexavar, skip the missed dose, and take your next dose at your regular time. Do not double your dose of Nexavar.
- If you take too much Nexavar call your doctor or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away.
What are the possible side effects of Nexavar?
Nexavar may cause serious side effects, including:
- decreased blood flow to the heart, heart attack and heart failure. Get emergency help right away if you get symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, racing heartbeat, swelling in lower legs, feet and abdomen, feel lightheaded or faint, tiredness, nausea, vomiting, or sweat a lot.
- increased risk of bleeding. Bleeding is a common side effect of Nexavar that can be serious and can lead to death. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have any signs of bleeding during treatment with Nexavar.
- high blood pressure. High blood pressure is a common side effect of Nexavar and can be serious.Your blood pressure should be checked every week during the first 6 weeks of starting Nexavar. Your blood pressure should be checked regularly and any high blood pressure should be treated during treatment with Nexavar.
- skin problems. A condition called hand-foot skin reactions and skin rash are common with Nexavar treatment and can be severe.Nexavar may also cause severe skin and mouth reactions that can be life-threatening. Tell your healthcare provider if you have any of the following symptoms:
- skin rash
- skin redness
- pain or swelling
- blistering and peeling of your skin
- blistering and peeling on the inside of your mouth
- blisters on the palms of your hand or soles of your feet
- an opening in the wall of your stomach or intestines (gastrointestinal perforation). Tell your healthcare provider right away if you get fever, nausea, vomiting or severe stomach (abdominal) pain.
- risk of wound healing problems. Wounds may not heal properly during Nexavar treatment. Tell your healthcare provider if you plan to have any surgery before starting or during treatment with Nexavar.
- You should stop taking Nexavar at least 10 days before planned surgery.
- Your healthcare provider should tell you when you may start taking Nexavar again after surgery.
- changes in the electrical activity of your heart called QT prolongation. QT prolongation can cause irregular heartbeats that can be life-threatening. Your healthcare provider may do tests during your treatment with Nexavar to check the levels of potassium, magnesium, and calcium in your blood, and check the electrical activity of your heart with an electrocardiogram (ECG). Tell your healthcare provider right away if you feel faint, lightheaded, dizzy or feel your heart beating irregularly or fast during your treatment with Nexavar.
- liver problems (drug-induced hepatitis). Nexavar may cause liver problems that may lead to liver failure and death. Your healthcare provider will do blood tests to check your liver function regularly during your treatment with Nexavar. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you develop any of the following symptoms.
- change in thyroid hormone levels. If you have differentiated thyroid cancer, you can have changes in your thyroid hormone levels during treatment with Nexavar. Your healthcare provider may need to change your dose of thyroid medicine during treatment with Nexavar. Your healthcare provider should check your thyroid hormone levels every month during treatment with Nexavar
The most common side effects of Nexavar include:
Nexavar may cause fertility problems in males. This may affect your ability to father a child. Talk to your healthcare provider if this is a concern for you.
These are not all of the possible side effects of Nexavar. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects.You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088
Label
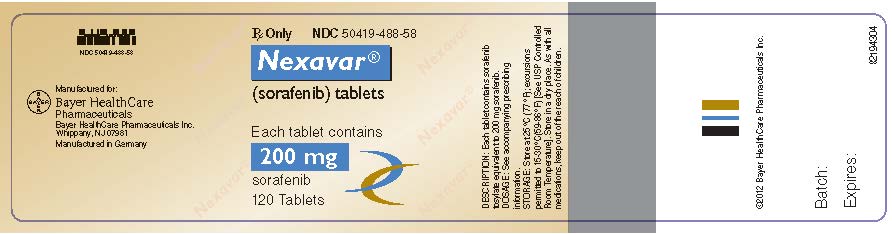
PACKAGE/LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
- Nexavar 200 mg Bottle Label
- Rx Only
- NDC 50419-488-58
- Nexavar®
(sorafenib) tablets - Each tablet contains
200 mg
sorafenib - 120 Tablets

General information about the safe and effective use of Nexavar
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use Nexavar for a condition for which it is not prescribed. Do not give Nexavar to other people even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about Nexavar that is written for health professionals.
How should I store Nexavar?
- Store Nexavar tablets at room temperature between 68° F to 77° F (20° C to 25° C).
- Store Nexavar tablets in a dry place.
- Keep Nexavar and all medicines out of the reach of children.
What are the ingredients in Nexavar?
Active Ingredient: sorafenib tosylate
Inactive Ingredients: croscarmellose sodium, ferric oxide red, hypromellose, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, sodium lauryl sulphate, polyethylene glycol, and titanium dioxide.