Propecia
Generic name: finasteride
Drug class: 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors
Medically reviewed by A Ras MD.
What is Propecia?
Propecia is a prescription medicine used for the treatment of male pattern hair loss (androgenetic alopecia).
It is not known if Propecia works for a receding hairline on either side of and above your forehead (temporal area).
Propecia is for use by MEN ONLY and should NOT be used by women or children.
Description
PROPECIA (finasteride) tablets contain finasteride as the active ingredient. Finasteride, a synthetic 4-azasteroid compound, is a specific inhibitor of steroid Type II 5α-reductase, an intracellular enzyme that converts the androgen testosterone into 5α-dihydrotestosterone (DHT).
The chemical name of finasteride is N-tert-Butyl-3-oxo-4-aza-5α-androst-1-ene-17β-carboxamide. The empirical formula of finasteride is C23H36N2O2 and its molecular weight is 372.55. Its structural formula is:
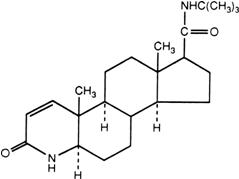
Finasteride is a white crystalline powder with a melting point near 250°C. It is freely soluble in chloroform and in lower alcohol solvents but is practically insoluble in water.
PROPECIA (finasteride) tablets are film-coated tablets for oral administration. Each tablet contains 1 mg of finasteride and the following inactive ingredients: lactose monohydrate, microcrystalline cellulose, pregelatinized starch, sodium starch glycolate, hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, hydroxypropyl cellulose, titanium dioxide, magnesium stearate, talc, docusate sodium, yellow ferric oxide, and red ferric oxide.
Mechanism of Action
Finasteride is a competitive and specific inhibitor of Type II 5α-reductase, an intracellular enzyme that converts the androgen testosterone into DHT. Two distinct isozymes are found in mice, rats, monkeys, and humans: Type I and II. Each of these isozymes is differentially expressed in tissues and developmental stages. In humans, Type I 5α-reductase is predominant in the sebaceous glands of most regions of skin, including scalp, and liver. Type I 5α-reductase is responsible for approximately one-third of circulating DHT. The Type II 5α-reductase isozyme is primarily found in prostate, seminal vesicles, epididymides, and hair follicles as well as liver, and is responsible for two-thirds of circulating DHT.
In humans, the mechanism of action of finasteride is based on its preferential inhibition of the Type II isozyme. Using native tissues (scalp and prostate), in vitro binding studies examining the potential of finasteride to inhibit either isozyme revealed a 100-fold selectivity for the human Type II 5α-reductase over Type I isozyme (IC50=500 and 4.2 nM for Type I and II, respectively). For both isozymes, the inhibition by finasteride is accompanied by reduction of the inhibitor to dihydrofinasteride and adduct formation with NADP+. The turnover for the enzyme complex is slow (t1/2 approximately 30 days for the Type II enzyme complex and 14 days for the Type I complex). Inhibition of Type II 5α-reductase blocks the peripheral conversion of testosterone to DHT, resulting in significant decreases in serum and tissue DHT concentrations.
In men with male pattern hair loss (androgenetic alopecia), the balding scalp contains miniaturized hair follicles and increased amounts of DHT compared with hairy scalp. Administration of finasteride decreases scalp and serum DHT concentrations in these men. The relative contributions of these reductions to the treatment effect of finasteride have not been defined. By this mechanism, finasteride appears to interrupt a key factor in the development of androgenetic alopecia in those patients genetically predisposed.
Who should not take Propecia?
Do not take Propecia if you:
- Are pregnant or may become pregnant. Propecia may harm your unborn baby.
- Propecia tablets are coated and will prevent contact with the medicine during handling, as long as the tablets are not broken or crushed. Females who are pregnant or who may become pregnant should not come in contact with broken or crushed Propecia tablets. If a pregnant woman comes in contact with crushed or broken Propecia tablets, wash the contact area right away with soap and water. If a woman who is pregnant comes into contact with the active ingredient in Propecia, a healthcare provider should be consulted.
- If a woman who is pregnant with a male baby swallows or comes in contact with the medicine in Propecia, the male baby may be born with sex organs that are not normal.
- Are allergic to any of the ingredients in Propecia. See the end of this medication guide for a complete list of ingredients in Propecia.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking Propecia?
Before taking Propecia, tell your healthcare provider if you:
- have any other medical conditions, including problems with your prostate or liver
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and non-prescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I take Propecia?
- Take Propecia exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to take it.
- You may take Propecia with or without food.
- If you forget to take Propecia, do not take an extra tablet. Just take the next tablet as usual.
Propecia will not work faster or better if you take it more than once a day.
What are the possible side effects of Propecia?
- decrease in your blood Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) levels. Propecia can affect a blood test called PSA (Prostate-Specific Antigen) for the screening of prostate cancer. If you have a PSA test done you should tell your healthcare provider that you are taking Propecia because Propecia decreases PSA levels. Changes in PSA levels will need to be evaluated by your healthcare provider. Any increase in follow-up PSA levels from their lowest point may signal the presence of prostate cancer and should be evaluated, even if the test results are still within the normal range for men not taking Propecia. You should also tell your healthcare provider if you have not been taking Propecia as prescribed because this may affect the PSA test results. For more information, talk to your healthcare provider.
- There may be an increased risk of a more serious form of prostate cancer in men taking finasteride at 5 times the dose of Propecia.
The most common side effects of Propecia include:
- decrease in sex drive
- trouble getting or keeping an erection
- a decrease in the amount of semen
The following have been reported in general use with Propecia:
- breast tenderness and enlargement. Tell your healthcare provider about any changes in your breasts such as lumps, pain or nipple discharge
- depression
- decrease in sex drive that continued after stopping the medication
- allergic reactions including rash, itching, hives and swelling of the lips, tongue, throat, and face
- problems with ejaculation that continued after stopping medication
- testicular pain
- difficulty in achieving an erection that continued after stopping the medication
- male infertility and/or poor quality of semen
- in rare cases, male breast cancer
Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all the possible side effects of Propecia. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
General information about the safe and effective use of Propecia.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in this Patient Information guide. Do not use Propecia for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Propecia to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them.
This Patient Information guide summarizes the most important information about Propecia. If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about Propecia that is written for health professionals. For more information, call 1-888-637-2522.
How should I store Propecia?
- Store Propecia at room temperature between 59°F to 86°F (15°C to 30°C).
- Keep Propecia in a closed container and keep Propecia tablets dry (protect from moisture).
Keep Propecia and all medicines out of the reach of children.
What are the ingredients in Propecia?
Active ingredient: finasteride.
Inactive ingredients: lactose monohydrate, microcrystalline cellulose, pregelatinized starch, sodium starch glycolate, hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, hydroxypropyl cellulose, titanium dioxide, magnesium stearate, talc, docusate sodium, yellow ferric oxide, and red ferric oxide.
Label
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 1 MG TABLET BOTTLE LABEL
- NDC 78206-152-01
- Propecia®
(finasteride) Tablets
1 mg - Each tablet contains 1 mg finasteride.
Warning: PROPECIA® (finasteride) should
not be used by women or children. Women
who are or may potentially be pregnant
must not use PROPECIA. They should also
not handle crushed or broken tablets of
PROPECIA. (See Package Insert.) - Rx only
- 30 Tablets

SRC: NLM .