Seroquel
Generic name: quetiapine
Brand names: SEROquel, SEROquel XR
Drug class: Atypical antipsychotics
Medically reviewed by A Ras MD.
What is Seroquel?
Seroquel is a prescription medicine used to treat schizophrenia in people 13 years of age or older and bipolar disorder in adults bipolar disorder in adults, including depressive episodes associated with bipolar disorder, manic episodes associated with bipolar I disorder alone or with lithium or divalproex, long-term treatment of bipolar I disorder with lithium or divalproex, manic episodes associated with bipolar I disorder in children ages 10-17 years old
It is not known if Seroquel is safe and effective in children under 10 years of age.
Description
SEROQUEL® (quetiapine) is an atypical antipsychotic belonging to a chemical class, the dibenzothiazepine derivatives. The chemical designation is 2-[2-(4-dibenzo [b,f] [1,4]thiazepin-11-yl-1-piperazinyl)ethoxy]-ethanol fumarate (2:1) (salt). It is present in tablets as the fumarate salt. All doses and tablet strengths are expressed as milligrams of base, not as fumarate salt. Its molecular formula is C42H50N6O4S2•C4H4O4 and it has a molecular weight of 883.11 (fumarate salt). The structural formula is:
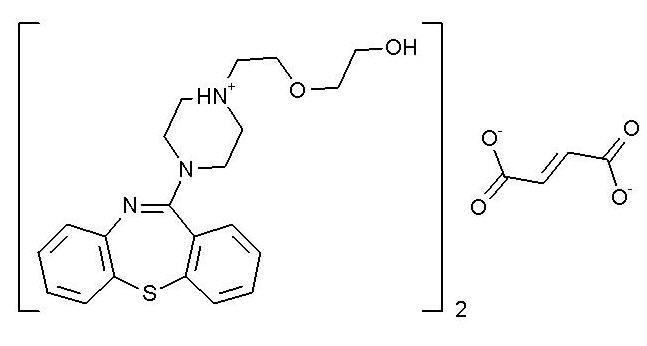
Quetiapine fumarate is a white to off-white crystalline powder which is moderately soluble in water.
SEROQUEL is supplied for oral administration as 25 mg (round, peach), 50 mg (round, white), 100 mg (round, yellow), 200 mg (round, white), 300 mg (capsule-shaped, white), and 400 mg (capsule-shaped, yellow) tablets.
Inactive ingredients are povidone, dibasic dicalcium phosphate dihydrate, microcrystalline cellulose, sodium starch glycolate, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, hypromellose, polyethylene glycol, and titanium dioxide.
The 25 mg tablets contain red ferric oxide and yellow ferric oxide and the 100 mg and 400 mg tablets contain only yellow ferric oxide.
Each 25 mg tablet contains 28.78 mg of quetiapine fumarate equivalent to 25 mg quetiapine. Each 50 mg tablet contains 57.56 mg of quetiapine fumarate equivalent to 50 mg quetiapine. Each 100 mg tablet contains 115.13 mg of quetiapine fumarate equivalent to 100 mg quetiapine. Each 200 mg tablet contains 230.26 mg of quetiapine fumarate equivalent to 200 mg quetiapine. Each 300 mg tablet contains 345.39 mg of quetiapine fumarate equivalent to 300 mg quetiapine. Each 400 mg tablet contains 460.51 mg of quetiapine fumarate equivalent to 400 mg quetiapine.
Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action of quetiapine in the listed indications is unclear. However, the efficacy of quetiapine in these indications could be mediated through a combination of dopamine type 2 (D2) and serotonin type 2 (5HT2) antagonism. The active metabolite, N-desalkyl quetiapine (norquetiapine), has similar activity at D2, but greater activity at 5HT2A receptors, than the parent drug (quetiapine).
What is the most important information I should know about Seroquel?
Seroquel may cause serious side effects, including:
1. Risk of death in the elderly with dementia. Medicines like Seroquel can increase the risk of death in elderly people who have memory loss (dementia). Seroquel is not for treating psychosis in the elderly with dementia.
2. Risk of suicidal thoughts or actions (antidepressant medicines, depression and other serious mental illnesses, and suicidal thoughts or actions)
- Talk to your or your family member’s healthcare provider about:
- all risks and benefits of treatment with antidepressant medicines.
- all treatment choices for depression or other serious mental illness
- Antidepressant medications may increase suicidal thoughts or actions in some children, teenagers, and young adults within the first few months of treatment.
- Depression and other serious mental illnesses are the most important causes of suicidal thoughts and actions. Some people may have a particularly high risk of having suicidal thoughts or actions. These include people who have (or have a family history of) depression, bipolar illness (also called manic-depressive illness), or suicidal thoughts or actions.
- How can I watch for and try to prevent suicidal thoughts and actions in myself or a family member?
- Pay close attention to any changes, especially sudden changes, in mood, behaviors, thoughts, or feelings. This is very important when an antidepressant medicine is started or when the dose is changed.
- Call the healthcare provider right away to report new or sudden changes in mood, behavior, thoughts, or feelings.
- Keep all follow-up visits with the healthcare provider as scheduled. Call the healthcare provider between visits as needed, especially if you have concerns about symptoms.
- Call a healthcare provider right away if you or your family member has any of the following symptoms, especially if they are new, worse, or worry you:
- thoughts about suicide or dying
- attempts to commit suicide
- new or worse depression
- new or worse anxiety
- feeling very agitated or restless
- panic attacks
- trouble sleeping (insomnia)
- new or worse irritability
- acting aggressive, being angry, or violent
- acting on dangerous impulses
- an extreme increase in activity and talking (mania)
- other unusual changes in behavior or mood
What else do I need to know about antidepressant medicines?
- Never stop an antidepressant medicine without first talking to your healthcare provider. Stopping an antidepressant medicine suddenly can cause other symptoms.
- Antidepressants are medicines used to treat depression and other illnesses. It is important to discuss all the risks of treating depression, and also the risks of not treating it. Patients and their families or other caregivers should discuss all treatment choices with the healthcare provider, not just the use of antidepressants.
- Antidepressant medicines have other side effects. Talk to the healthcare provider about the side effects of the medicine prescribed for you or your family member.
- Antidepressant medicines can interact with other medicines. Know all of the medicines that you or your family member take. Keep a list of all medicines to show the healthcare provider. Do not start new medicines without first checking with your healthcare provider.
- Not all antidepressant medicines prescribed for children are FDA approved for use in children. Talk to your child’s healthcare provider for more information.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking Seroquel?
Before you take Seroquel, tell your healthcare provider if you have or have had:
- diabetes or high blood sugar in you or your family. Your healthcare provider should check your blood sugar before you start Seroquel, and also during therapy
- high levels of total cholesterol, triglycerides or LDL-cholesterol, or low levels of HDL-cholesterol
- low or high blood pressure
- low white blood cell count
- cataracts
- seizures
- abnormal thyroid tests
- high prolactin levels
- heart problems
- liver problems
- any other medical condition
- pregnancy or plans to become pregnant. It is not known if Seroquel will harm your unborn baby.
- If you become pregnant while receiving Seroquel, talk to your healthcare provider about registering with the National Pregnancy Registry for Atypical Antipsychotics. You can register by calling 1-866-961-2388 or go to https://womensmentalhealth.org/research/pregnancyregistry/atypicalantipsychotic/
- breast-feeding or plans to breast-feed. Seroquel can pass into your breast milk. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby if you receive Seroquel.
- if you have or have had a condition where you cannot completely empty your bladder (urinary retention), have an enlarged prostate, or constipation, or increased pressure inside your eyes.
Tell the healthcare provider about all the medicines that you take or recently have taken including prescription medicines, over-the-counter medicines, herbal supplements, and vitamins.
Seroquel and other medicines may affect each other causing serious side effects. Seroquel may affect the way other medicines work, and other medicines may affect how Seroquel works.
Tell your healthcare provider if you are having a urine drug screen because Seroquel may affect your test results. Tell those giving the test that you are taking Seroquel.
How should I take Seroquel?
- Take Seroquel exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to take it. Do not change the dose yourself.
- Take Seroquel by mouth, with or without food.
- If you feel you need to stop Seroquel, talk with your healthcare provider first. If you suddenly stop taking Seroquel, you may have side effects such as trouble sleeping or trouble staying asleep (insomnia), nausea, and vomiting.
- If you miss a dose of Seroquel, take it as soon as you remember. If you are close to your next dose, skip the missed dose. Just take the next dose at your regular time. Do not take 2 doses at the same time unless your healthcare provider tells you to. If you are not sure about your dosing, call your healthcare provider.
What should I avoid while taking Seroquel?
- Do not drive, operate machinery, or do other dangerous activities until you know how Seroquel affects you. Seroquel may make you drowsy.
- Avoid getting overheated or dehydrated
- Do not over-exercise.
- In hot weather, stay inside in a cool place if possible. Stay out of the sun.
- Do not wear too much or heavy clothing.
- Drink plenty of water.
- Do not drink alcohol while taking Seroquel. It may make some side effects of Seroquel worse.
What are possible side effects of Seroquel?
Seroquel can cause serious side effects, including:
- See also “What is the most important information I should know about Seroquel?”
- Stroke that can lead to death can happen in elderly people with dementia who take medicines like Seroquel
- Neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS). NMS is a rare but very serious condition that can happen in people who take antipsychotic medicines, including Seroquel. NMS can cause death and must be treated in a hospital. Call your healthcare provider right away if you become severely ill and have some or all of these symptoms:
- high fever
- excessive sweating
- rigid muscles
- confusion
- changes in your breathing, heartbeat, and blood pressure
- Falls can happen in some people who take Seroquel. These falls may cause serious injuries.
- High blood sugar (hyperglycemia). High blood sugar can happen if you have diabetes already or if you have never had diabetes. High blood sugar could lead to abuild-up of acid in your blood due to ketones (ketoacidosis), coma and death. Increases in blood sugar can happen in some people who take Seroquel. Extremely high blood sugar can lead to coma or death. If you have diabetes or risk factors for diabetes (such as being overweight or a family history of diabetes) your healthcare provider should check your blood sugar before you start Seroquel and during therapy. Call your healthcare provider if you have any of these symptoms of high blood sugar (hyperglycemia) while taking Seroquel:
- feel very thirsty
- need to urinate more than usual
- feel very hungry
- feel weak or tired
- feel sick to your stomach
- feel confused, or your breath smells fruity
- high fat levels in your blood (increased cholesterol and triglycerides). High fat levels may happen in people treated with Seroquel. You may not have any symptoms, so your healthcare provider may decide to check your cholesterol and triglycerides during your treatment with Seroquel.
- increase in weight (weight gain). Weight gain is common in people who take Seroquel so you and your healthcare provider should check your weight regularly. Talk to your healthcare provider about ways to control weight gain, such as eating a healthy, balanced diet, and exercising.
- movements you cannot control in your face, tongue, or other body parts (tardive dyskinesia). These may be signs of a serious condition. Tardive dyskinesia may not go away, even if you stop taking Seroquel. Tardive dyskinesia may also start after you stop taking Seroquel.
- decreased blood pressure (orthostatic hypotension), including lightheadedness or fainting caused by a sudden change in heart rate and blood pressure when rising too quickly from a sitting or lying position.
- increases in blood pressure in children and teenagers. Your healthcare provider should check blood pressure in children and adolescents before starting Seroquel and during therapy.
- low white blood cell count. Tell your healthcare provider as soon as possible if you have a fever, flu-like symptoms, or any other infection, as this could be a result of a very low white blood cell count. Your healthcare provider may check your white blood cell level to determine if further treatment or other action is needed.
- cataracts
- seizures
- abnormal thyroid tests. Your healthcare provider may do blood tests to check your thyroid hormone level.
- increases in prolactin levels
- sleepiness, drowsiness, feeling tired, difficulty thinking and doing normal activities
- increased body temperature
- difficulty swallowing
- trouble sleeping or trouble staying asleep (insomnia), nausea, or vomiting if you suddenly stop taking Seroquel. These symptoms usually get better 1 week after you start having them.
The most common side effects of Seroquel include:
In adults:
- drowsiness
- sudden drop in blood pressure upon standing
- weight gain
- sluggishness
- abnormal liver tests
- upset stomach
- dry mouth
- dizziness
- weakness
- abdominal pain
- constipation
- sore throat
In children and adolescents:
- drowsiness
- dizziness
- fatigue
- nausea
- dry mouth
- weight gain
- increased appetite
- vomiting
- rapid heart beat
These are not all the possible side effects of Seroquel. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
Drug Interactions
A total of 674 medications are known to interact with Seroquel. Use the Interactions Checker Tool.
Common Interactions Checks
- clonazepam
- Cymbalta
- gabapentin
- Klonopin
- Lamictal
- Lexapro
- lisinopril
- omeprazole
- trazodone
- Vitamin D3
- Xanax
- Zoloft
General information about the safe and effective use of Seroquel
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use Seroquel for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Seroquel to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them.
This Medication Guide summarizes the most important information about Seroquel. If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about Seroquel that is written for health professionals.
For more information call 1-800-236-9933.
How should I store Seroquel?
- Store Seroquel at room temperature, between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- Keep Seroquel and all medicines out of the reach of children.
What are the ingredients in Seroquel?
Active ingredient: quetiapine fumarate
Inactive ingredients: povidone, dibasic dicalcium phosphate dihydrate, microcrystalline cellulose, sodium starch glycolate, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, hypromellose, polyethylene glycol, and titanium dioxide. The 25 mg tablets contain red and yellow ferric oxide. The 100 mg and 400 mg tablets contain only yellow ferric oxide.
Label
PACKAGE/LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 25 MG
- NDC 0310-0275-10 100 tablets
- SeroQUEL®
- (quetiapine) tablets
- 25 mg*
- Rx only
- Medication Guide must be
- dispensed to patients.
- AstraZeneca


PACKAGE/LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 50 MG
- NDC 0310-0278-10 100 tablets
- SeroQUEL®
- (quetiapine) tablets
- 50 mg*
- Rx only
- Medication Guide must be
- dispensed to patients.
- AstraZeneca


PACKAGE/LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 100 MG
- NDC 0310-0271-10 100 tablets
- SeroQUEL®
- (quetiapine) tablets
- 100 mg*
- Rx only
- Medication Guide must be
- dispensed to patients.
- AstraZeneca


PACKAGE/LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 200 MG
- NDC 0310-0272-10 100 tablets
- SeroQUEL®
- (quetiapine) tablets
- 200 mg*
- Rx only
- Medication Guide must be
- dispensed to patients.
AstraZeneca


PACKAGE/LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 300 MG
- NDC 0310-0274-60 60 tablets
- SeroQUEL®
- (quetiapine) tablets
- 300 mg*
- Rx only
- Medication Guide must be
- dispensed to patients.
- AstraZeneca


PACKAGE/LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 400 MG
- NDC 0310-0279-10 100 tablets
- SeroQUEL®
- (quetiapine) tablets
- 400 mg*
- Rx only
- Medication Guide must be
- dispensed to patients.
- AstraZeneca


SRC: NLM .